4.3 Compute and plot PCA (Principal Component Analysis)
Reshape the data for PCA.
pca_data <- protein_data_parsed_mut %>%
select(Identifier, Reference, Intensity) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = Identifier, values_from = Intensity) %>%
column_to_rownames(var = "Reference") %>%
select(where(~ !any(is.na(.)))) %>% # remove columns with NA values.
select(where(~ var(.) > 0)) # remove columns with zero variance.Perform the PCA.
Get the percentage of variance explained by each principal component.
Create a data frame for plotting.
pca_df <- as.data.frame(pca_result$x) %>%
rownames_to_column(var = "Reference") %>%
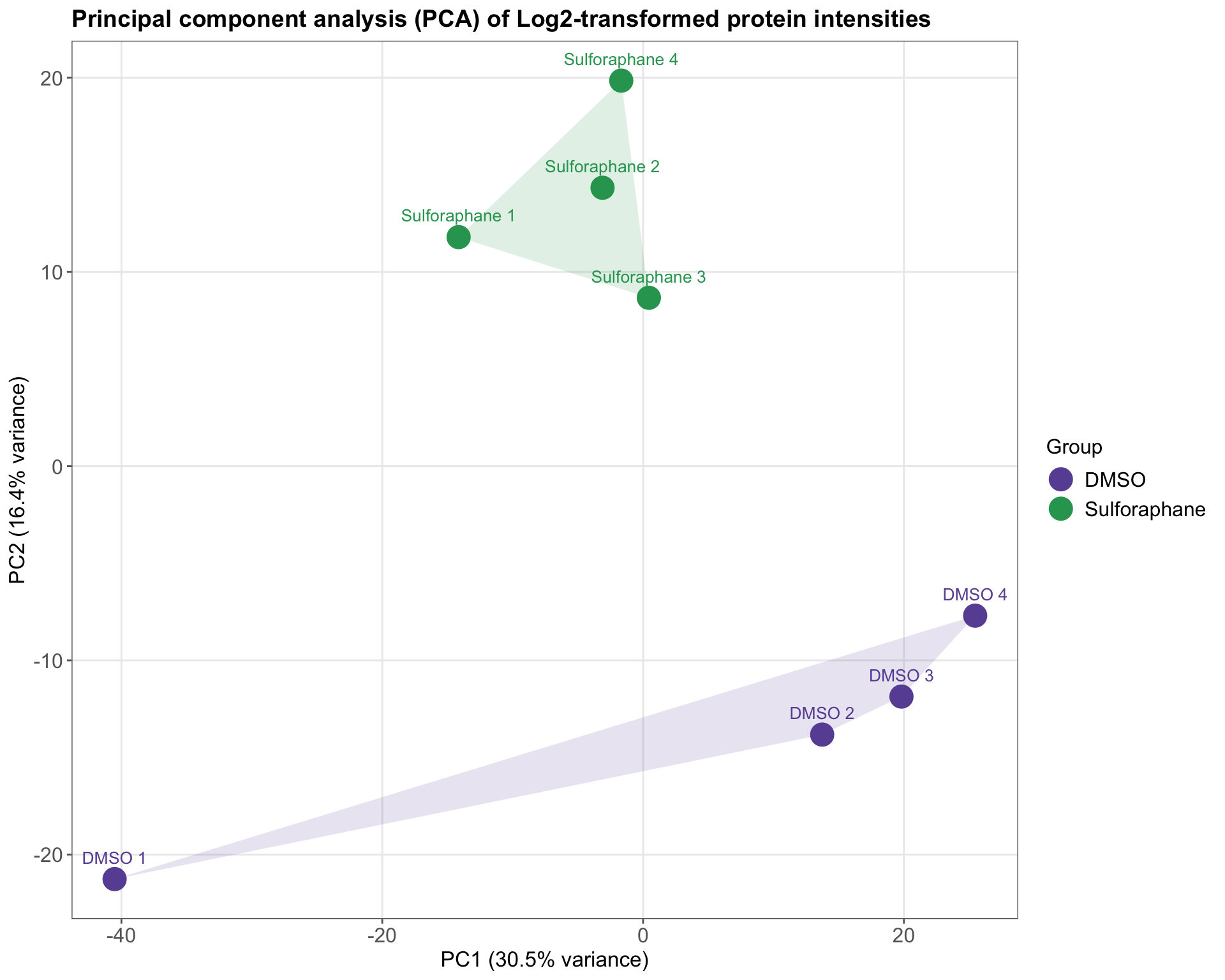
mutate(Label = if_else(str_detect(Reference, "DMSO"), "DMSO", "Sulforaphane"))Take a look at the PCA data frame that will be used for plotting.
## Reference PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4
## 1 DMSO 1 -40.5236994 -21.263605 -9.643622 2.0643358
## 2 DMSO 2 13.7332455 -13.822736 13.220601 0.9806235
## 3 DMSO 3 19.8122465 -11.864672 5.863109 -0.0572881
## 4 DMSO 4 25.4636747 -7.697248 -16.619225 -7.6995175
## 5 Sulforaphane 1 -14.1460645 11.793599 19.907967 -21.5451863
## 6 Sulforaphane 2 -3.1087881 14.334322 6.820141 17.9491878
## 7 Sulforaphane 3 0.4434575 8.669353 2.249586 15.2578529
## 8 Sulforaphane 4 -1.6740722 19.850987 -21.798556 -6.9500080
## PC5 PC6 PC7 PC8 Label
## 1 -0.9507316 1.258466 -1.05864899 2.506960e-13 DMSO
## 2 14.0553245 -18.934979 -0.02030233 2.459518e-13 DMSO
## 3 8.2225187 22.743865 2.39521208 2.462277e-13 DMSO
## 4 -18.5430187 -4.678309 -5.77878509 2.423448e-13 DMSO
## 5 -7.3112721 1.097554 0.33856664 2.473822e-13 Sulforaphane
## 6 -2.2533926 1.808497 -18.20934008 2.490623e-13 Sulforaphane
## 7 -10.0897930 -2.272283 20.13713178 2.485977e-13 Sulforaphane
## 8 16.8703647 -1.022810 2.19616600 2.491229e-13 SulforaphanePlotting pipeline:
Calculate convex hulls for each group (optional). These are used to draw fancy polygons around the groups in the PCA plot.
Start ggplot, map global aesthetics (x and y axes, color, and labels)
Add points layer
Add polygon layer for convex hulls around the groups
Add text (point labels) layer
Add labels and titles for axes and legend
Customize colors for points and polygons
Apply minimal theme and further customize it
# Calculate convex hulls for each group (optional)
hulls <- pca_df %>%
group_by(Label) %>%
slice(chull(PC1, PC2)) %>%
ungroup()ggplot(pca_df, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, color = Label, label = Reference)) +
geom_point(size = 6) +
# Draw convex hulls around the groups
geom_polygon(
data = hulls, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, fill = Label, color = Label),
alpha = 0.15, color = NA, show.legend = FALSE
) +
geom_text(vjust = -1.3, hjust = 0.5, size = 3.5, show.legend = FALSE) +
labs(
title = "Principal component analysis (PCA) of Log2-transformed protein intensities",
x = paste0("PC1 (", round(pca_variance[1], 1), "% variance)"),
y = paste0("PC2 (", round(pca_variance[2], 1), "% variance)"),
color = "Group"
) +
scale_color_manual(values = label_colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = label_colors) +
theme_minimal() +
# Further customize the theme
theme(
axis.text = element_text(size = 12, color = "#666666"),
axis.title = element_text(size = 12.5),
plot.title = element_text(size = 14, face = "bold"),
legend.title = element_text(size = 12),
legend.text = element_text(size = 12),
legend.position = "right",
panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
panel.border = element_rect(color = "#666666", fill = NA),
axis.ticks = element_line(color = "#666666")
)